Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Contractility
Contractility refers to the ability of muscle fibers to shorten and generate force when stimulated. This property is essential for muscle movement and is a direct result of the interaction between actin and myosin filaments within the muscle cells. The strength and speed of contraction can vary based on the type of muscle and the conditions under which it operates.
Recommended video:
Contractile Tissue: Molecular Physiology
Excitability
Excitability is the capacity of muscle cells to respond to stimuli, such as nerve impulses or hormonal signals. This property allows muscles to initiate contraction when they receive an appropriate signal, making it fundamental for coordinated movement and reflex actions. The excitability of muscle tissue is primarily due to the presence of specialized ion channels in the cell membrane.
Recommended video:
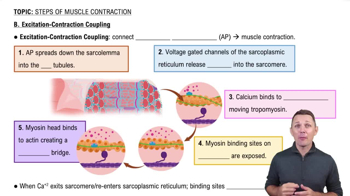
B. Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Elasticity
Elasticity is the ability of muscle tissue to return to its original shape after being stretched or contracted. This property is crucial for maintaining muscle tone and ensuring that muscles can efficiently respond to repeated contractions without damage. Elasticity allows muscles to absorb and release energy, contributing to overall functional performance during physical activities.
Recommended video: