Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
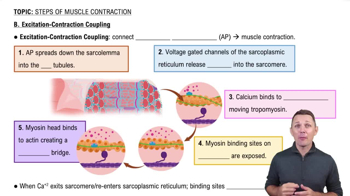
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Excitation-contraction coupling refers to the physiological process by which an electrical signal (action potential) in a muscle cell leads to muscle contraction. This process begins when a nerve impulse triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which then interact with the contractile proteins, actin and myosin, enabling muscle fibers to shorten and generate force.
Recommended video:
B. Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Role of Calcium Ions
Calcium ions play a crucial role in excitation-contraction coupling by acting as a signaling molecule. When released into the cytoplasm, calcium binds to troponin, causing a conformational change that moves tropomyosin away from the binding sites on actin filaments. This exposure allows myosin heads to attach to actin, facilitating the cross-bridge cycle that results in muscle contraction.
Recommended video:
Ions - Sodium and Potassium Example 3
Action Potential
An action potential is a rapid, temporary change in the electrical membrane potential of a cell, which is essential for initiating muscle contraction. In muscle cells, the action potential travels along the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules, triggering the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This electrical signal is the first step in the chain of events leading to muscle contraction.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance