Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Muscle Tissue Types
There are three primary types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is striated and under voluntary control, primarily attached to bones for movement. Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, is also striated but operates involuntarily to pump blood. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary, located in walls of hollow organs like the intestines and blood vessels, facilitating various bodily functions.
Recommended video:
Structure of Muscle Tissue
The structure of muscle tissues varies significantly. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, cylindrical, and multi-nucleated, allowing for powerful contractions. Cardiac muscle cells are branched and interconnected, featuring intercalated discs that enable synchronized contractions. Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped and lack striations, allowing for more gradual and sustained contractions in response to various stimuli.
Recommended video:
Organization of Muscle Tissue
Functions of Muscle Tissue
Each muscle tissue type serves distinct functions. Skeletal muscle is responsible for voluntary movements and posture. Cardiac muscle's primary function is to contract rhythmically to circulate blood throughout the body. Smooth muscle controls involuntary movements, such as peristalsis in the digestive tract and regulating blood vessel diameter, contributing to homeostasis.
Recommended video:
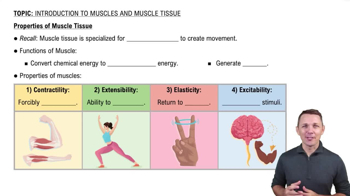
Properties of Muscle Tissue