Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Smooth Muscle Types
Smooth muscle is classified into two main types: multi-unit and unitary. Multi-unit smooth muscle consists of individual muscle fibers that operate independently, while unitary smooth muscle fibers are connected by gap junctions, allowing them to function as a single unit. This distinction is crucial for understanding how different smooth muscle types respond to stimuli.
Recommended video:
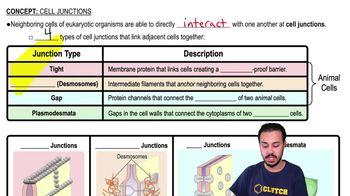
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections that allow for direct communication between adjacent cells. In unitary smooth muscle, these junctions enable the rapid transmission of electrical signals, facilitating coordinated contractions across the muscle tissue. This feature is essential for the rhythmic contractions seen in organs like the intestines and bladder.
Recommended video:
Pacemaker Cells
Pacemaker cells are specialized cells that generate spontaneous electrical impulses, initiating contractions in smooth muscle. In the context of unitary smooth muscle, these cells help regulate the rhythmic activity of the muscle, ensuring that organs such as the digestive tract and urinary bladder contract in a coordinated manner to facilitate their functions.
Recommended video:
Comparing Action Potentials in Pacemaker and Contractile Cells
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance