Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is characterized by its composition of a large amount of extracellular matrix, which provides structural support and protection to organs and tissues. It includes various types such as bone, blood, and adipose tissue, each serving distinct functions in the body. The matrix can vary in consistency, influencing the tissue's properties and roles.
Recommended video:
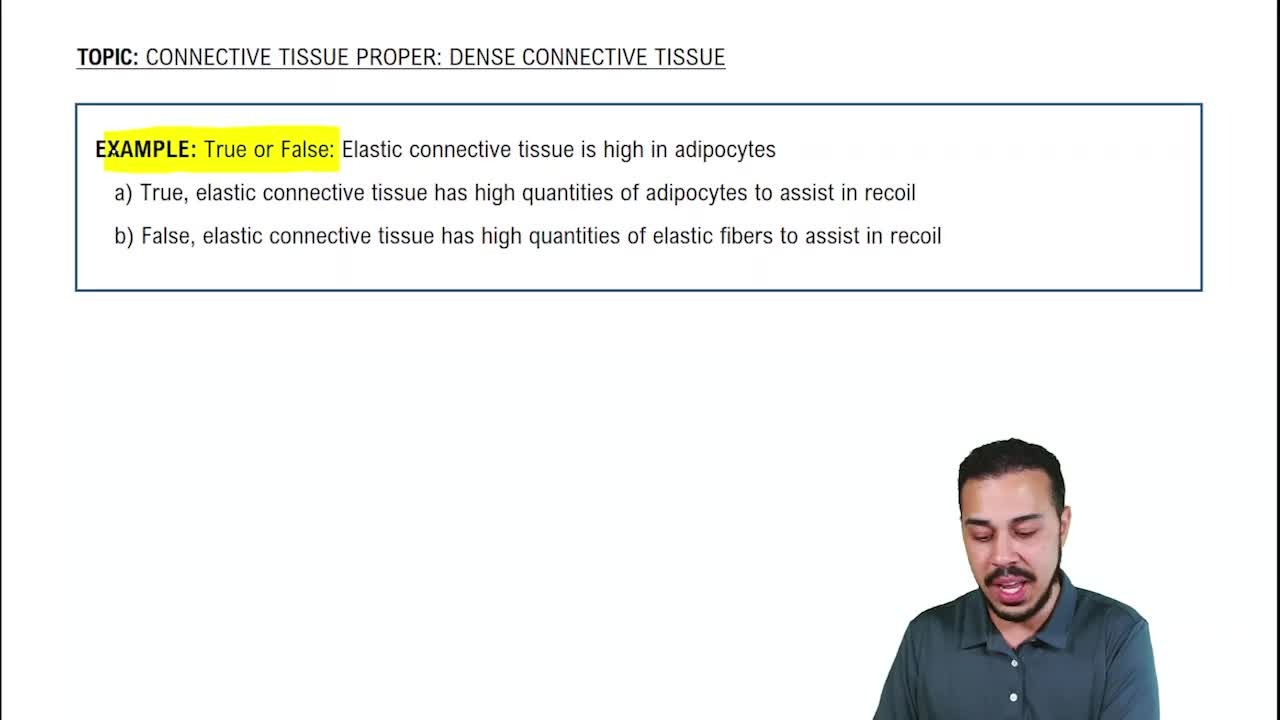
Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective Tissue Example 3
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is specialized for contraction and is responsible for body movement. There are three types: skeletal muscle, which moves bones; cardiac muscle, which makes up the heart; and smooth muscle, found in walls of hollow organs. Each type has unique structural features that enable its specific functions in movement and control.
Recommended video:
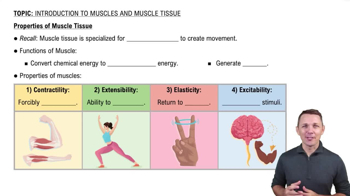
Properties of Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is essential for communication within the body, consisting of neurons and glial cells. Neurons transmit electrical signals, allowing for rapid responses to stimuli, while glial cells support and protect neurons. This tissue is crucial for processing sensory information and coordinating bodily responses to the environment.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance