Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
First Law of Thermodynamics
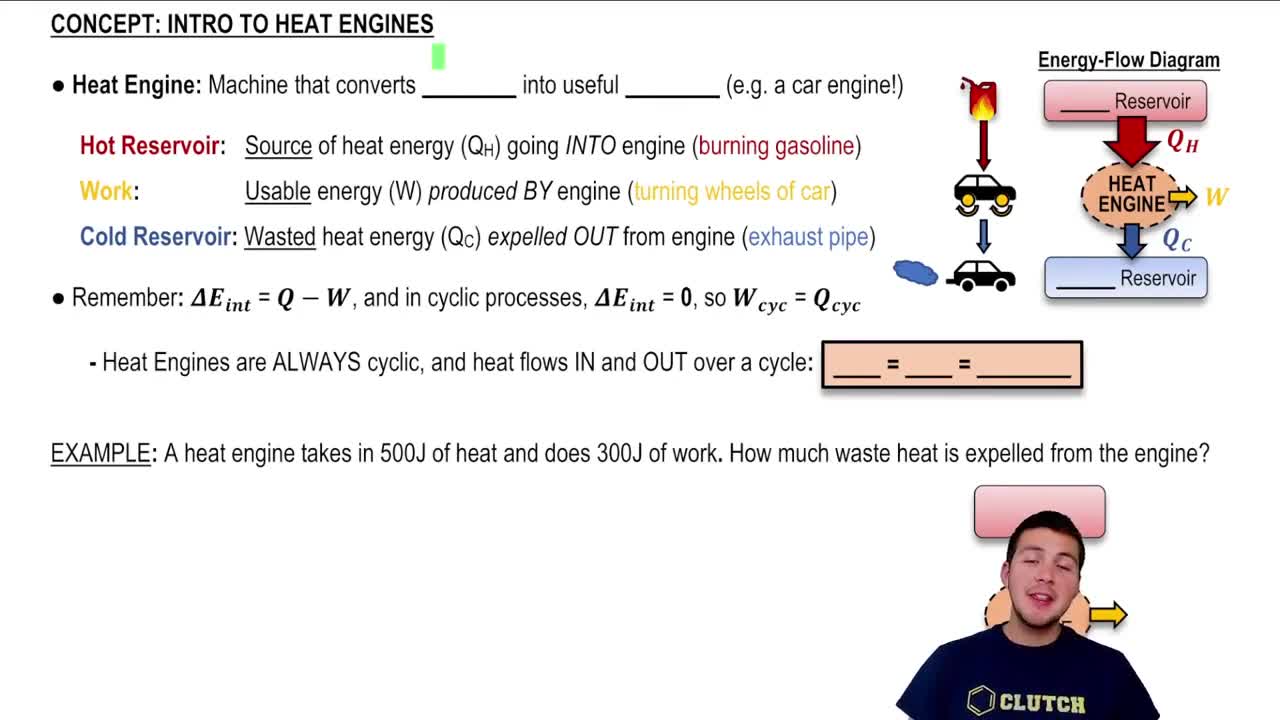
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In the context of heat engines, this means that the total energy input must equal the total energy output, accounting for work done and heat transferred. If a heat engine claims to produce more energy than it consumes, it would violate this law.
Recommended video:
The First Law of Thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics introduces the concept of entropy, stating that in any energy transfer or transformation, the total entropy of a closed system can never decrease over time. This implies that heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body without external work. A heat engine that operates in a way that decreases the overall entropy of the system would violate this law.
Recommended video:
Thermal Efficiency & The Second Law of Thermodynamics
Heat Engine Efficiency
The efficiency of a heat engine is defined as the ratio of work output to heat input, often expressed as a percentage. It is influenced by the temperatures of the heat reservoirs involved. According to the Second Law, no heat engine can be 100% efficient, as some energy is always lost as waste heat. Analyzing the efficiency of the engines in the question will help determine if they adhere to thermodynamic principles.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Heat Engines