Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
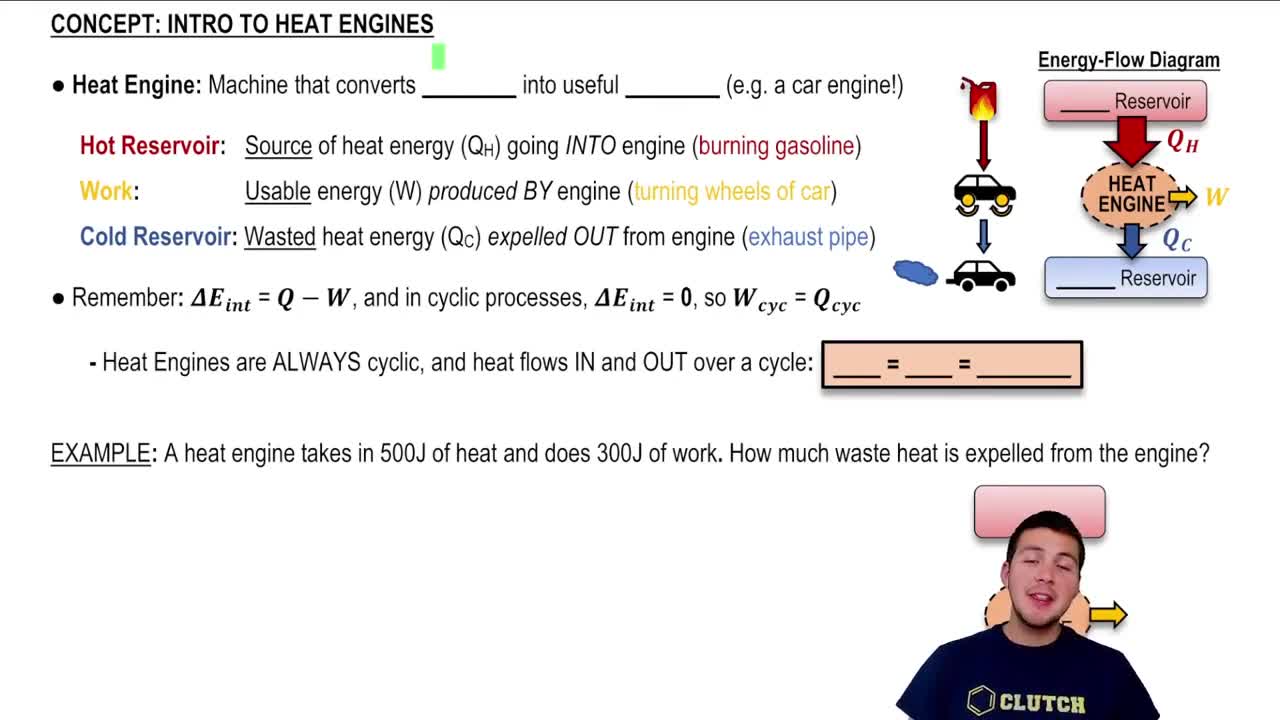
Heat Engine
A heat engine is a device that converts thermal energy into mechanical work by exploiting the temperature difference between a hot reservoir and a cold reservoir. The efficiency of a heat engine is determined by the temperatures of these reservoirs and the specific thermodynamic cycle it operates on, such as the Carnot cycle or the Otto cycle.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Heat Engines
Thermodynamic Efficiency
Thermodynamic efficiency is a measure of how well a heat engine converts heat from the fuel into work. It is defined as the ratio of the work output to the heat input, often expressed as a percentage. The efficiency can be influenced by factors such as the temperature difference between the heat reservoirs and the specific heat capacities of the working substance.
Recommended video:
Thermal Efficiency & The Second Law of Thermodynamics
Power Output
Power output refers to the rate at which work is done by the engine, typically measured in watts (W). It can be calculated by multiplying the work done in one cycle by the number of cycles per second. In the context of a heat engine, understanding the power output is crucial for evaluating its performance and efficiency in converting heat energy into useful work.
Recommended video:
Power Output of a Gasoline Engine