Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Carnot Efficiency
Carnot efficiency is the maximum possible efficiency of a heat engine operating between two thermal reservoirs. It is defined by the formula η = 1 - (T_c / T_h), where η is the efficiency, T_c is the absolute temperature of the cold reservoir, and T_h is the absolute temperature of the hot reservoir. This concept illustrates the theoretical limits of efficiency based on temperature differences.
Recommended video:
The Carnot Cycle and Maximum Theoretical Efficiency
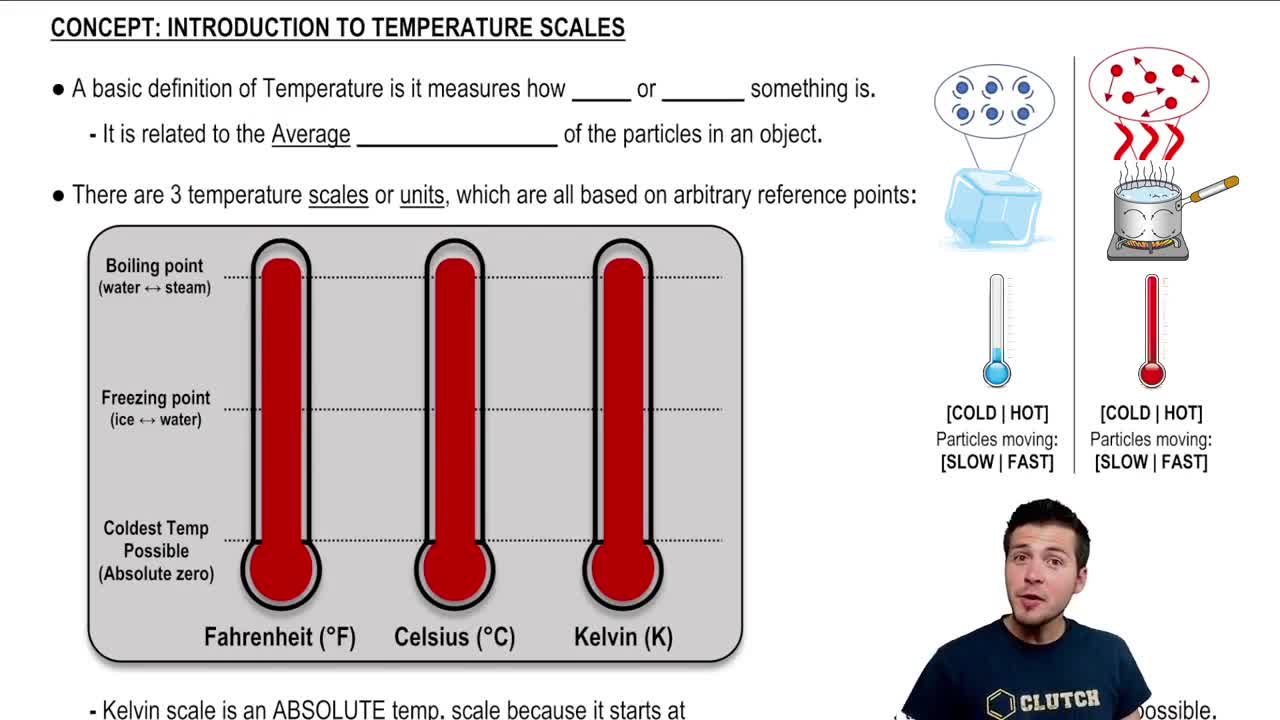
Absolute Temperature
Absolute temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) and is a scale that starts at absolute zero, the point where molecular motion ceases. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15. In the context of the Carnot engine, both the hot and cold reservoir temperatures must be expressed in Kelvin to accurately calculate efficiency and understand thermodynamic principles.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
Thermodynamic Temperature Scale
The thermodynamic temperature scale is a scale that reflects the energy state of a system and is crucial for understanding heat engines. It is based on the laws of thermodynamics and is measured in Kelvin. This scale is essential for calculating efficiencies and understanding the behavior of heat engines, as it provides a consistent framework for comparing temperatures across different systems.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance