What is a chemical element?
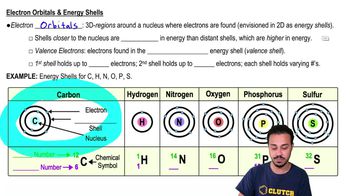
DRAW IT Diagram the electronic configuration of a carbon atom.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
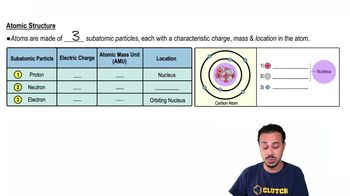
Atomic Structure
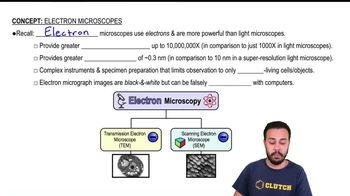
Electron Configuration
Orbital Diagrams
Radioisotopes are frequently used to label molecules in a cell. The fate of atoms and molecules in a cell can then be followed. This process is the basis for questions 1-3.
Assume E. coli bacteria are grown in a nutrient medium containing the radioisotope ¹⁶N. After a 48-hour incubation period, the ¹⁶N would most likely be found in the E. coli’s
a. carbohydrates.
b. lipids.
c. proteins.
d. water.
e. none of the above
Classify each of the molecules on the left as an acid, base, or salt. The dissociation products of the molecules are shown to help you.
MgSO₄ → Mg²⁺ + SO²₄⁻
Radioisotopes are frequently used to label molecules in a cell. The fate of atoms and molecules in a cell can then be followed. This process is the basis for questions 1-3.
If Pseudomonas bacteria are supplied with radioactively labeled cytosine, after a 24-hour incubation period this cytosine would most likely be found in the cells’
a. carbohydrates.
b. DNA.
c. lipids.
d. water.
e. proteins.
What type of bond holds the following atoms together?
a. Li+ and Cl- in LiCl
b. carbon and oxygen atoms in methanol
c. oxygen atoms in O₂
d. a hydrogen atom of one nucleotide to a nitrogen or oxygen atom of another nucleotide in:
<IMAGE>
Radioisotopes are frequently used to label molecules in a cell. The fate of atoms and molecules in a cell can then be followed. This process is the basis for questions 1-3.
If E. coli were grown in a medium containing the radioactive isotope ³²P, the ³²P would be found in all of the following molecules of the cell except
a. ATP.
b. carbohydrates.
c. DNA.
d. plasma membrane.
e. complex lipids.
