Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Radioisotopes in Biological Research
Radioisotopes, such as ¹⁶N, are unstable isotopes that emit radiation as they decay. In microbiology, they are used to trace the incorporation of specific atoms into biological molecules, allowing researchers to study metabolic pathways and cellular processes. By labeling molecules with radioisotopes, scientists can track their fate within cells, providing insights into how organisms utilize nutrients.
Recommended video:
Nitrogen's Role in Biomolecules
Nitrogen is a crucial element found in amino acids, nucleotides, and other biomolecules. In E. coli, nitrogen from the nutrient medium is incorporated into proteins and nucleic acids, which are essential for growth and reproduction. Understanding how nitrogen is assimilated into these molecules helps explain the metabolic functions of bacteria and their growth requirements.
Recommended video:
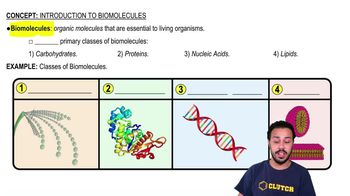
Introduction to Biomolecules
Metabolic Pathways in E. coli
E. coli utilizes various metabolic pathways to synthesize biomolecules from available nutrients. When grown in a medium containing ¹⁶N, the bacteria will incorporate this nitrogen into proteins, nucleic acids, and other nitrogen-containing compounds. Recognizing these pathways is essential for predicting where the labeled nitrogen will be found after incubation, as it reflects the organism's metabolic activity and nutrient utilization.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Metabolism
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance