Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
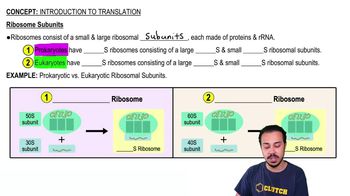
Macromolecule Subunits
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules essential for life, and they are classified into four main types: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each type is composed of specific subunits; for example, carbohydrates are made of monosaccharides, proteins are made of amino acids, lipids consist of fatty acids and glycerol, and nucleic acids are formed from nucleotides.
Recommended video:
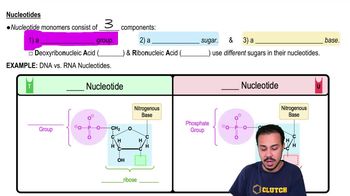
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (like thymine), a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose in DNA), and a phosphate group. Thymine is specifically a pyrimidine base found in DNA, and its presence indicates the nucleotide's role in genetic information storage.
Recommended video:
Classification of Biological Molecules
The classification of biological molecules is crucial for understanding their functions and interactions in biological systems. Each macromolecule type has distinct roles; for instance, carbohydrates provide energy, lipids store energy and form cell membranes, proteins perform a wide range of functions including catalysis and structure, and nucleic acids are responsible for genetic information storage and transfer.
Recommended video: