Textbook Question
Draw the structures of adenine and uracil (which replaces thymine in RNA), and show the hydrogen bonding that occurs between them.
10
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

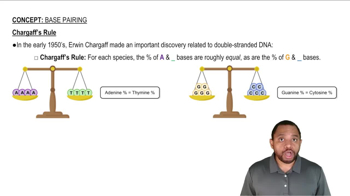

Draw the structures of adenine and uracil (which replaces thymine in RNA), and show the hydrogen bonding that occurs between them.
(a) DNA and RNA, like proteins, can be denatured to produce unfolded or uncoiled strands. Heating DNA to what is referred to as its “melting temperature” denatures it (the two strands of the double helix become separated). Why does a longer strand of DNA have a higher melting temperature than a shorter one?
a. What is meant by the term base pairing?
The DNA from sea urchins contains about 32% A and about 18% G. What percentages of T and C would you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.