Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
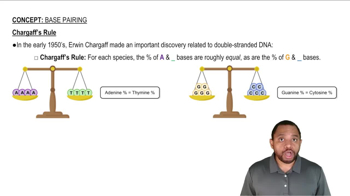
Base Pairing Rules
In DNA, the base pairing rules dictate that guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C), and adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T). This means that the amount of G in a double-stranded DNA molecule will equal the amount of C, and the amount of A will equal the amount of T. Understanding these rules is essential for calculating the percentages of the other bases when one is known.
Recommended video:
Chargaff's Rules
Chargaff's rules state that in a double-stranded DNA molecule, the ratio of adenine to thymine and the ratio of guanine to cytosine are equal. This principle helps in determining the composition of DNA, as knowing the percentage of one base allows for the calculation of the others. For example, if G is 22%, then C must also be 22%, leading to further deductions about A and T.
Recommended video:
Percentage Composition of DNA Bases
The percentage composition of DNA bases refers to the relative amounts of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine in a DNA molecule. In a double-stranded DNA, the total percentage of A and T combined must equal the total percentage of G and C combined. This concept is crucial for solving problems related to base composition, as it allows for the calculation of unknown percentages based on known values.
Recommended video:
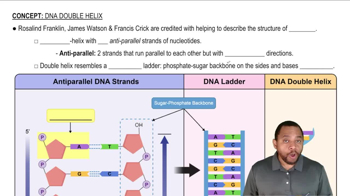
DNA Double Helix Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance