Identify the following carbohydrates as the α or ß anomer:
(b) <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Identify the following carbohydrates as the α or ß anomer:
(b) <IMAGE>
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of the oxidation of d-galactose at C1.
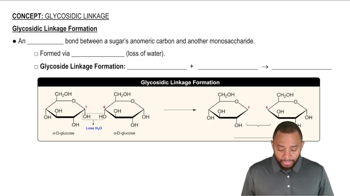
Draw the product of the following 1→4 condensation and name the glycosidic bond:
<IMAGE> + <IMAGE> →
d-Fructose can also form a six-membered ring. Draw the anomer of d-fructose in the six-membered ring form.
Classify each of the following monosaccharides by the type of carbonyl group and the number of carbons (for example, a monosaccharide with an aldehyde and three carbons is an aldotriose).
(a) <IMAGE>
Classify each of the following monosaccharides by the type of carbonyl group and the number of carbons (for example, a monosaccharide with an aldehyde and three carbons is an aldotriose).
(a) <IMAGE>