Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
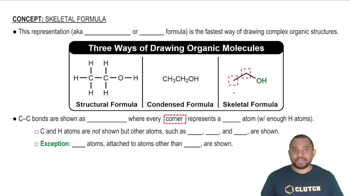
Skeletal Structures
Skeletal structures, or line-angle formulas, are simplified representations of organic molecules where carbon atoms are represented by vertices and hydrogen atoms are implied. This notation omits the explicit depiction of hydrogen atoms attached to carbons, making it easier to visualize complex organic compounds. Understanding how to read and draw these structures is essential for accurately representing molecular connectivity.
Recommended video:
Skeletal Formula Concept 1
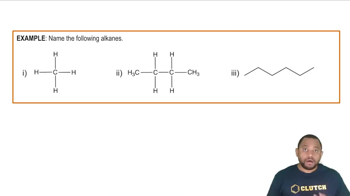
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons consisting only of carbon and hydrogen atoms, connected by single bonds. They follow the general formula CnH2n+2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Recognizing the characteristics of alkanes, such as their structural variations and nomenclature, is crucial for drawing their skeletal structures correctly.
Recommended video:
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method for naming organic chemical compounds based on their structure. It provides rules for identifying the longest carbon chain, substituents, and their positions, which is essential for accurately interpreting compound names like 2,3-dimethylpentane. Familiarity with these naming conventions is vital for translating chemical names into their corresponding skeletal structures.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance