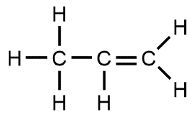
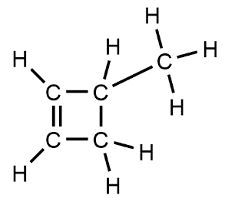
Organic chemistry focuses on the study of carbon-containing compounds, emphasizing their structure, properties, and reactions. A defining characteristic of organic compounds is the presence of carbon atoms bonded to each other (C-C bonds) and to hydrogen atoms (C-H bonds). Compounds that consist solely of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. However, many organic compounds also incorporate other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens.
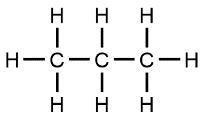
For instance, propane is a simple hydrocarbon composed of three carbon atoms, each bonded to hydrogen atoms. It is commonly found in propane tanks used for barbecues and other applications. Ethanol, another organic compound, includes an -OH (hydroxyl) group in addition to its carbon and hydrogen framework. This compound is notably present in alcoholic beverages like wine.
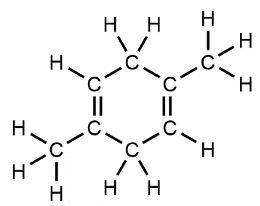
More complex organic compounds include caffeine, which contains carbon and nitrogen atoms, as well as multiple double bonds. Caffeine is a well-known stimulant found in coffee. Another example is geraniol, a compound found in roses, which features both double bonds and an -OH group, alongside its carbon and hydrogen structure.
In summary, organic chemistry encompasses a wide range of compounds characterized by carbon's ability to form stable bonds with itself and other elements, leading to a diverse array of structures and functionalities. Understanding these compounds is essential for exploring their reactions and applications in everyday life.