Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lac Operon
The lac operon is a set of genes in E. coli that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It consists of structural genes that encode proteins necessary for lactose uptake and breakdown, regulated by a promoter and operator. The operon is inducible, meaning it is activated in the presence of lactose, allowing the bacteria to utilize this sugar when glucose is scarce.
Recommended video:
CAP Protein and cAMP
The CAP (catabolite activator protein) is a transcription factor that enhances the transcription of the lac operon in the presence of cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate). When glucose levels are low, cAMP levels rise, allowing CAP to bind to the CAP-binding site on the lac promoter, facilitating RNA polymerase binding and increasing gene expression. A mutation in the crp gene, which encodes CAP, would reduce this activation.
Recommended video:
Mutations in Regulatory Elements
Mutations in regulatory elements, such as the CAP-binding site within the lac operon promoter, can significantly affect gene expression. If the CAP-binding site is disrupted, even if CAP is present, it cannot bind effectively, leading to decreased transcription of the lac operon. This illustrates how specific DNA sequences are crucial for the proper regulation of gene expression in response to environmental signals.
Recommended video:
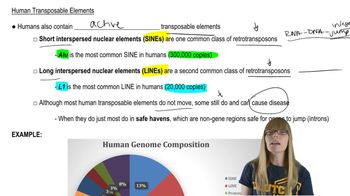
Human Transposable Elements