Textbook Question
Water flows quickly through the narrow neck of a bottle, but maple syrup flows sluggishly. Is this different behavior due to a difference in viscosity or in surface tension for the liquids?
351
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
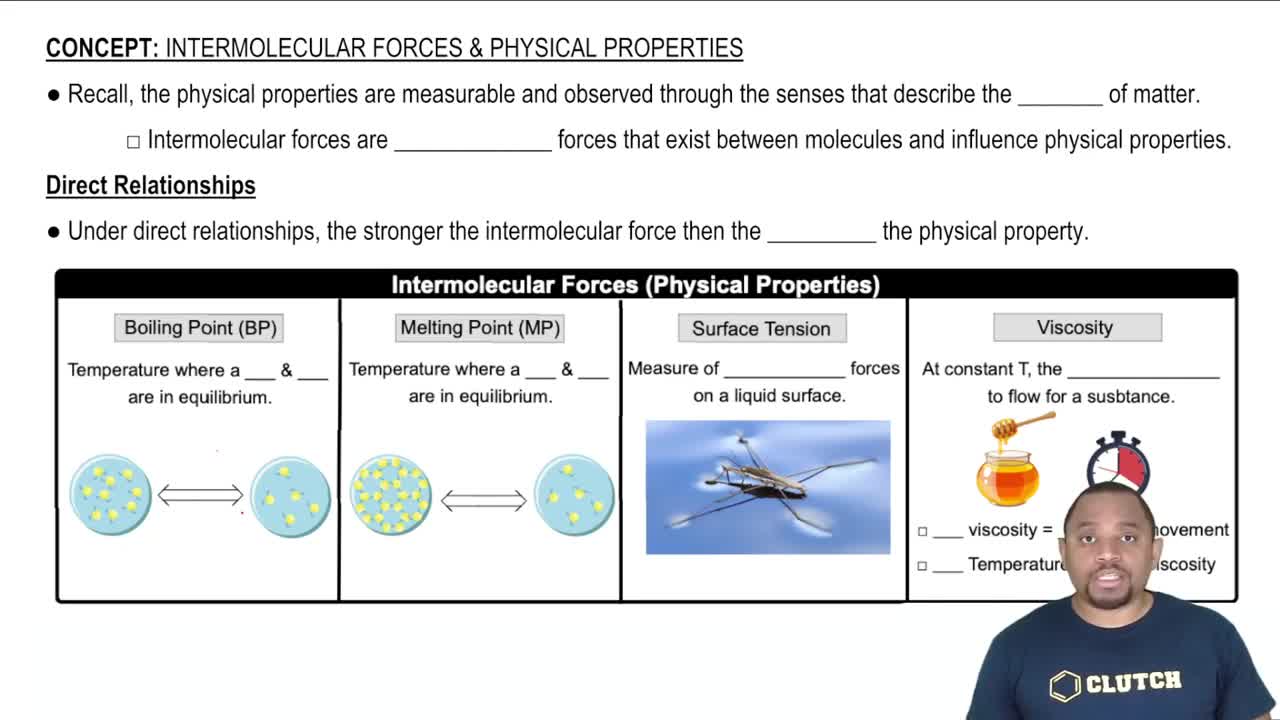


Predict which substance in each pair has the highest viscosity. (a) Hexane 1CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH32 or 1-hexanol 1CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH2