Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
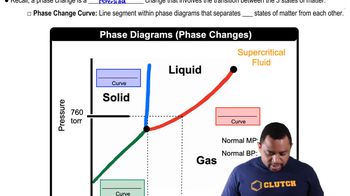
Phase Diagrams
Phase diagrams are graphical representations that show the state of a substance (solid, liquid, or gas) at various temperatures and pressures. They help visualize the conditions under which different phases coexist and transition into one another. Understanding how to read and interpret phase diagrams is crucial for predicting the behavior of substances like benzene under varying temperature and pressure conditions.
Recommended video:
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Critical Point
The critical point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the distinction between liquid and gas phases disappears. Beyond this point, the substance enters a supercritical state, where it exhibits properties of both phases. For benzene, the critical temperature (Tc) is 289.01 °C, and the critical pressure (Pc) is 48.34 atm, which are essential for understanding the transitions that occur during the path traced in the question.
Recommended video:
Phase Transitions
Phase transitions refer to the changes between solid, liquid, and gas states of a substance, driven by variations in temperature and pressure. Each transition, such as melting, boiling, or sublimation, occurs at specific conditions. In the context of the question, tracking the changes in temperature and pressure allows us to determine the starting and final phases of benzene as it undergoes these transitions.
Recommended video:
Phase Changes in Diagrams