Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces between molecules that influence physical properties such as boiling and melting points. The main types include hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces. Understanding these forces is crucial for analyzing the behavior of substances, particularly in states of matter like liquids and solids.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is covalently bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. In the compound shown, the presence of the -COOH (carboxylic acid) and -NH2 (amine) groups allows for significant hydrogen bonding, which contributes to the compound's solubility and structural properties in liquid crystals.
Recommended video:
Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystals are materials that exhibit properties between those of liquids and solid crystals. They have ordered molecular arrangements that can change in response to temperature or electric fields. The intermolecular forces present in liquid crystals, such as hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces, play a critical role in maintaining their unique phases and behaviors, making them essential in applications like displays and sensors.
Recommended video:
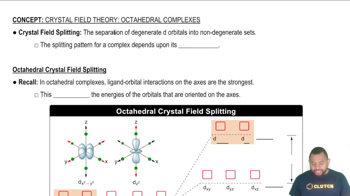
The crystal field splitting pattern for octahedral complexes has the d orbitals on or along the axes as having the higher energy.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance