Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Liquid Crystal Phases
Liquid crystals are materials that exhibit properties between those of liquids and solid crystals. They can flow like a liquid but have some degree of order, particularly in their molecular arrangement. The transition between solid and liquid crystal states involves changes in temperature and can be influenced by molecular structure and interactions.
Recommended video:
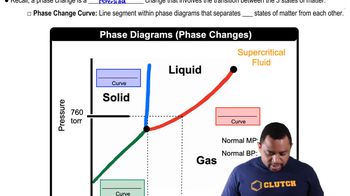
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Phase Transition Temperature
The phase transition temperature is the specific temperature at which a substance changes from one phase to another, such as from solid to liquid crystal. This temperature is influenced by intermolecular forces, molecular weight, and structural characteristics of the compounds. Higher phase transition temperatures typically indicate stronger intermolecular interactions.
Recommended video:
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules. These forces, including hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and van der Waals forces, play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances, including their melting points and phase transition temperatures. Stronger intermolecular forces generally lead to higher phase transition temperatures.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces