Textbook Question
A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 3. (a) What are the possible values of ml for this orbital?
891
views




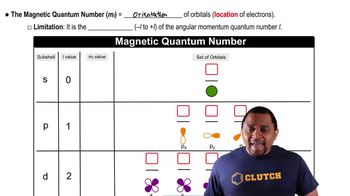
A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 3. (a) What are the possible values of ml for this orbital?
A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 3. (b) What are the possible values of ms for the orbital?
Which of the following represent impossible combinations of n and l? (a) 1p (b) 4s (c) 5f (d) 2d
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (a) s.
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (c) dx2 - y2.
(c) What can you say about the average distance from the nucleus of an electron in a 2s orbital as compared with a 3s orbital?