A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 3. (b) What are the possible values of ms for the orbital?
Ch.6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms
Chapter 6, Problem 63a
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (a) s.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that an 's' orbital is a type of atomic orbital that is spherical in shape.
Recognize that the 's' orbital is centered around the nucleus of an atom, with no directional preference, meaning it is non-directional.
Visualize the 's' orbital as a sphere where the probability of finding an electron is the same at any point equidistant from the nucleus.
Note that the size of the 's' orbital increases with the principal quantum number (n), so a 1s orbital is smaller than a 2s orbital, and so on.
Remember that the 's' orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, which must have opposite spins according to the Pauli exclusion principle.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Atomic Orbitals
Atomic orbitals are regions in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. They are defined by quantum mechanics and come in various shapes and sizes, corresponding to different energy levels. The most common types of orbitals are s, p, d, and f, each with unique characteristics that influence the chemical behavior of atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Atomic Orbitals Example
Shape of s Orbitals
s orbitals are spherical in shape and are the simplest type of atomic orbital. They have no angular nodes, meaning the probability of finding an electron is uniform in all directions around the nucleus. The size of the s orbital increases with the principal quantum number, indicating that higher energy s orbitals are larger and can accommodate electrons further from the nucleus.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Angular Momentum Quantum Number and Orbital Shape
Orientation of Orbitals
The orientation of orbitals refers to how they are positioned in three-dimensional space relative to each other. For s orbitals, there is no directional orientation since they are spherical. In contrast, p orbitals have specific orientations along the x, y, and z axes, which is important for understanding how atoms bond and interact in molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course
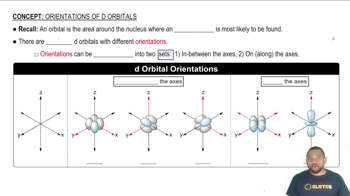
d Orbital Orientations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
559
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following represent impossible combinations of n and l? (a) 1p (b) 4s (c) 5f (d) 2d
1080
views
Textbook Question
For the table that follows, write which orbital goes with the quantum numbers. Don't worry about x, y, z subscripts. If the quantum numbers are not allowed, write 'not allowed.' n l ml Orbital 2 1 -1 2p (example) 1 0 0 3 -3 2 3 2 -2 2 0 -1 0 0 0 4 2 1 5 3 0
1056
views
Textbook Question
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (c) dx2 - y2.
533
views
Textbook Question
(c) What can you say about the average distance from the nucleus of an electron in a 2s orbital as compared with a 3s orbital?
677
views
Textbook Question
(d) For the hydrogen atom, list the following orbitals in order of increasing energy (that is, most stable ones first): 4f, 6s, 3d, 1s, 2p.
859
views
