Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (a) 3p.
Ch.6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms
Chapter 6, Problem 59a
A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 3. (a) What are the possible values of ml for this orbital?

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are a set of numerical values that describe the unique quantum state of an electron in an atom. The four quantum numbers are principal (n), azimuthal (l), magnetic (ml), and spin (ms). Each number provides specific information about the electron's energy level, shape, orientation, and spin, which are essential for understanding electron configurations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Principal Quantum Number
Principal Quantum Number (n)
The principal quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level or shell of an electron in an atom. It can take positive integer values (1, 2, 3, ...), with higher values corresponding to electrons that are further from the nucleus and have higher energy. In this case, n = 4 signifies that the electron is in the fourth energy level.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Principal Quantum Number
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
The magnetic quantum number (ml) describes the orientation of an orbital in space and can take on integer values ranging from -l to +l, where l is the azimuthal quantum number. For l = 3, which corresponds to an f orbital, ml can take values of -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, and +3, resulting in a total of seven possible orientations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
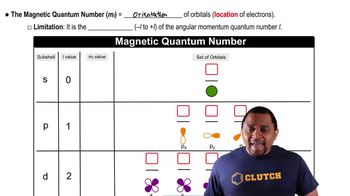
Magnetic Quantum Number
Related Practice
Textbook Question
505
views
Textbook Question
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (d) 5d.
791
views
Textbook Question
Give the values for n, l, and ml for (a) each orbital in the 3p subshell.
777
views
Textbook Question
A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 3. (b) What are the possible values of ms for the orbital?
559
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following represent impossible combinations of n and l? (a) 1p (b) 4s (c) 5f (d) 2d
1080
views
Textbook Question
For the table that follows, write which orbital goes with the quantum numbers. Don't worry about x, y, z subscripts. If the quantum numbers are not allowed, write 'not allowed.' n l ml Orbital 2 1 -1 2p (example) 1 0 0 3 -3 2 3 2 -2 2 0 -1 0 0 0 4 2 1 5 3 0
1056
views
