Repeat Exercise 12.51 for a linear chain of eight lithium atoms. (b) How many nodes are in the lowest-energy molecular orbital? (c) How many nodes are in the highestenergy molecular orbital? (d) How many nodes are in the highest-energy occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)? (e) How many nodes are in the lowest-energy unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)?
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials
Chapter 12, Problem 54
Which of the following statements does not follow from the fact that the alkali metals have relatively weak metal–metal bonding? (a) The alkali metals are less dense than other metals. (b) The alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife. (c) The alkali metals are more reactive than other metals. (d) The alkali metals have higher melting points than other metals. (e) The alkali metals have low ionization energies.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the general properties of alkali metals related to their weak metal-metal bonding. These properties include being soft, having low densities, low melting points, and low ionization energies.
Analyze each statement to see if it logically follows from the weak metal-metal bonding of alkali metals. Weak bonding generally leads to easier deformation (softness), lower density, and lower energy required to remove an electron (ionization energy).
Consider the statement about reactivity. Alkali metals are known for their high reactivity, which is influenced by their low ionization energies, allowing them to lose electrons easily.
Evaluate the statement regarding the melting points of alkali metals. Weak metal-metal bonding would suggest lower melting points because less energy is required to overcome the bonding between atoms.
Determine which statement does not logically follow from the premise of weak metal-metal bonding. A statement that contradicts the expected properties derived from weak bonding would be the correct choice.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Metal-Metal Bonding
Metal-metal bonding refers to the interactions between metal atoms in a solid. In alkali metals, these bonds are relatively weak due to their single valence electron, which leads to a less cohesive structure. This weakness contributes to their unique physical properties, such as lower density and softness compared to other metals.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Transition Metals
Reactivity of Alkali Metals
Alkali metals are known for their high reactivity, which is primarily due to their low ionization energies. This means they can easily lose their single valence electron to form positive ions. Their reactivity increases down the group, making them more reactive than many other metals, which is a key characteristic of these elements.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Transition Metals
Melting Points and Density
The melting points of alkali metals are generally lower than those of other metals, which is attributed to their weak metal-metal bonding. Additionally, their low density is a result of their atomic structure and the presence of these weak bonds. Understanding these properties helps in predicting the behavior of alkali metals in various conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
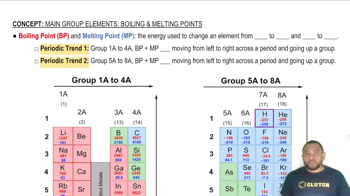
Boiling Point and Melting Point
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Repeat Exercise 12.51 for a linear chain of eight lithium atoms. (f) How does the HOMO–LUMO energy gap for this case compare to that of the four-atom case?
331
views
Textbook Question
Which would you expect to be the more ductile element, (a) Ag or Mo? (b) Zn or Si? In each case explain your reasoning.
563
views
Open Question
Arrange the following metals in increasing order of expected melting points: Mo, Zr, Y, Nb. Explain this trend in melting points.
Textbook Question
For each of the following groups, which metal would you
expect to have the highest melting point: (b) rubidium, molybdenum, or indium?
792
views
Textbook Question
Tausonite, a mineral composed of Sr, O, and Ti, has the cubic unit cell shown in the drawing. (a) What is the empirical formula of this mineral?
755
views
