Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Empirical Formula
The empirical formula of a compound represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements present in that compound. It is derived from the molecular formula by reducing the subscripts to their smallest values. For example, if a mineral contains Sr, O, and Ti in a ratio of 1:2:1, the empirical formula would be SrO2Ti.
Recommended video:
Empirical vs Molecular Formula
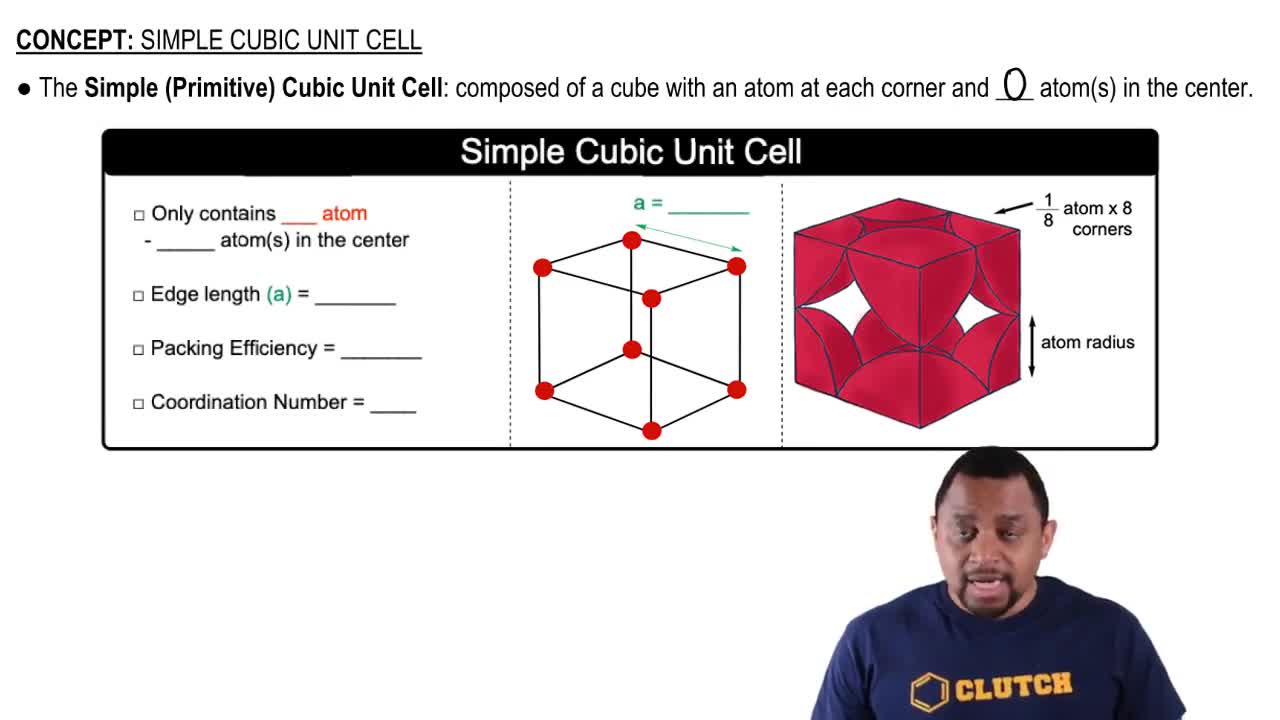
Cubic Unit Cell
A cubic unit cell is the smallest repeating unit in a crystal lattice that reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal. In the context of the question, the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure indicates that atoms are located at each corner and the centers of all the cube faces, which influences the arrangement and ratio of the constituent elements in the mineral.
Recommended video:
Stoichiometry in Minerals
Stoichiometry in minerals involves understanding the quantitative relationships between the different elements in a mineral's composition. By analyzing the arrangement of atoms in the unit cell, one can determine how many of each type of atom are present, which is essential for calculating the empirical formula of the mineral.
Recommended video: