The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (a) How many molecular orbitals are there in the diagram?
Repeat Exercise 12.51 for a linear chain of eight lithium atoms. (f) How does the HOMO–LUMO energy gap for this case compare to that of the four-atom case?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
HOMO-LUMO Energy Gap
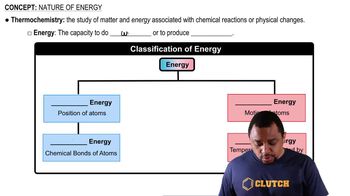
Molecular Orbital Theory

Size Dependence in Nanostructures

The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (c) How many nodes are in the highest-energy molecular orbital?
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (e) How many nodes are in the lowest-energy unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)?
Which would you expect to be the more ductile element, (a) Ag or Mo? In each case explain your reasoning.
Which of the following statements does not follow from the fact that the alkali metals have relatively weak metal–metal bonding? (a) The alkali metals are less dense than other metals. (b) The alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife. (c) The alkali metals are more reactive than other metals. (d) The alkali metals have higher melting points than other metals. (e) The alkali metals have low ionization energies.
