Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mechanism of Action of Oral Contraceptives
Oral contraceptives, commonly known as 'the pill,' primarily function by preventing ovulation. They contain synthetic hormones similar to progesterone and estradiol, which inhibit the release of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) from the pituitary gland. This suppression prevents the maturation and release of eggs from the ovaries, thereby reducing the likelihood of fertilization and pregnancy.
Recommended video:
Stages of Human Reproduction
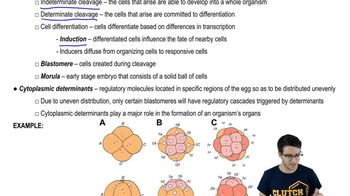
Human reproduction involves several key stages: ovulation, fertilization, cleavage, and implantation. Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovary. Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell unites with an egg. Cleavage is the series of cell divisions that occur after fertilization, and implantation is the attachment of the embryo to the uterine wall. Each stage is crucial for a successful pregnancy.
Recommended video:
Ethical and Social Considerations in Contraceptive Development
The development and approval of contraceptives often involve ethical and social considerations. In the U.S., contraceptives that prevent fertilization, such as those blocking ovulation, are generally less controversial because they prevent pregnancy before it begins. In contrast, methods that interfere with post-fertilization stages, like implantation, may raise ethical concerns about the beginning of life, making them more controversial.
Recommended video:
Cleavage and Blastulation