How is energy transferred among antenna pigment molecules?
a. By heat
b. By redox reactions
c. By fluorescence
d. By resonance

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
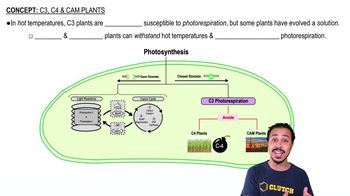

How is energy transferred among antenna pigment molecules?
a. By heat
b. By redox reactions
c. By fluorescence
d. By resonance
Why is chlorophyll green?
a. It absorbs all wavelengths in the visible spectrum.
b. It absorbs wavelengths only in the red portions of the spectrum (680–700 nm).
c. It absorbs wavelengths only in the blue part of the visible spectrum (450–480 nm).
d. It absorbs wavelengths in only the blue and red parts of the visible spectrum.
At what point in photosynthesis is the electromagnetic energy of light first converted into chemical energy?
Why is the chlorophyll in chloroplasts less likely to produce fluorescence compared to extracted chlorophyll molecules?
Describe the three phases of the Calvin cycle and how the products of the light-capturing reactions participate in this process.