Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polygenic Inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the genetic mechanism where multiple genes contribute to a single trait, resulting in a continuous range of phenotypes. Traits such as height, skin color, and seed color in plants often exhibit this pattern, as they are influenced by several alleles from different genes. In contrast to single-gene traits, polygenic traits do not follow simple Mendelian inheritance patterns.
Recommended video:
Genotype and Phenotype
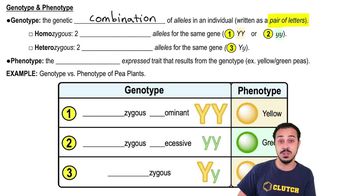
The genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism, represented by the alleles it possesses, while the phenotype is the observable expression of that genotype, influenced by both genetics and environmental factors. In the case of the round yellow pea seed with genotype RrYy, the phenotype would be round shape and yellow color, which are determined by the dominant alleles R (round) and Y (yellow).
Recommended video:
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics is the study of how traits are inherited through the principles established by Gregor Mendel, focusing on single-gene traits that follow specific inheritance patterns. Mendel's laws, including the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment, explain how alleles segregate during gamete formation and how different traits are inherited independently. The round yellow pea seed example involves two traits, but each trait is determined by a single gene, making it a case of dihybrid inheritance rather than polygenic inheritance.
Recommended video:
Mendelian and Population Genetics
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance