Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
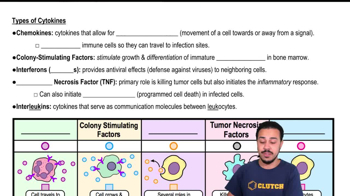
Cytokines
Cytokines are small proteins released by cells that have a specific effect on the interactions and communications between cells in the immune system. They play a crucial role in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. Different cytokines can promote or inhibit the activity of immune cells, influencing the overall response to pathogens.
Recommended video:
Types of Cytokines
Cytokines can be classified into several types, including interleukins, interferons, tumor necrosis factors, and chemokines. Each type has distinct functions; for example, interleukins are primarily involved in cell signaling, while interferons are critical for antiviral responses. Understanding these types helps in grasping how the immune system coordinates its response to infections.
Recommended video:
Immune Response
The immune response is the body's defense mechanism against pathogens, involving a complex network of cells and signaling molecules. It can be categorized into innate immunity, which provides immediate but non-specific defense, and adaptive immunity, which develops a targeted response over time. Cytokines are essential in mediating and regulating both types of immune responses, ensuring an effective reaction to infections.
Recommended video:
Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Problem 21
Problem 21 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance