Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Humoral Immunity
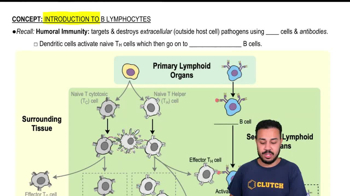
Humoral immunity is a component of the adaptive immune system that involves the production of antibodies by B cells. These antibodies circulate in the bloodstream and bind to specific antigens, neutralizing pathogens or marking them for destruction by other immune cells. This type of immunity is particularly effective against extracellular pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses in their free form.
Recommended video:
Cellular Immunity
Cellular immunity, also known as cell-mediated immunity, involves T cells that directly attack infected or cancerous cells. Unlike humoral immunity, which relies on antibodies, cellular immunity is crucial for eliminating intracellular pathogens, such as viruses that have invaded host cells. T cells can also help regulate the immune response and enhance the activity of other immune cells.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Cellular Respiration
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity is a specialized immune response that develops over time and provides long-lasting protection against specific pathogens. It is characterized by its ability to remember previous encounters with pathogens, allowing for a more rapid and effective response upon re-exposure. Both humoral and cellular immunity are integral parts of adaptive immunity, working together to provide comprehensive defense against infections.
Recommended video:
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Problem 23
Problem 23 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance