Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rami Communicantes
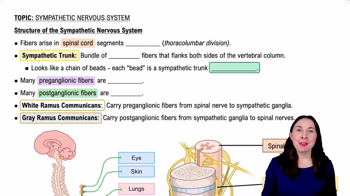
Rami communicantes are small nerve branches that connect the spinal nerves to the sympathetic trunk. They consist of two types: white rami communicantes, which carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers from the spinal nerve to the sympathetic ganglia, and gray rami communicantes, which carry postganglionic sympathetic fibers back to the spinal nerve. Understanding their role is crucial for comprehending the autonomic nervous system's organization.
Recommended video:
Structure of the Sympathetic Nervous System
Spinal Nerve Anatomy
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that contain both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) fibers. Each spinal nerve emerges from the spinal cord and divides into dorsal and ventral roots, which then combine to form the spinal nerve. The anatomical relationship between the spinal nerve and the rami communicantes is essential for understanding how autonomic signals are integrated with somatic functions.
Recommended video:
Types of Nerve Fibers
Nerve fibers can be classified based on their function: sensory fibers transmit information from the body to the central nervous system, while motor fibers carry signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands. In the context of rami communicantes, white rami contain myelinated preganglionic sympathetic fibers, while gray rami contain unmyelinated postganglionic sympathetic fibers, highlighting the differences in conduction velocity and function.
Recommended video:
3 Types of Protein Fibers
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance