Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Direct and Indirect Muscle Attachments
Direct muscle attachments, also known as fleshy attachments, occur when the muscle fibers attach directly to the bone, allowing for a strong connection. In contrast, indirect attachments involve tendons, which are fibrous connective tissues that connect muscles to bones, providing a more flexible and resilient link. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for comprehending how muscles exert force on bones during movement.
Recommended video:
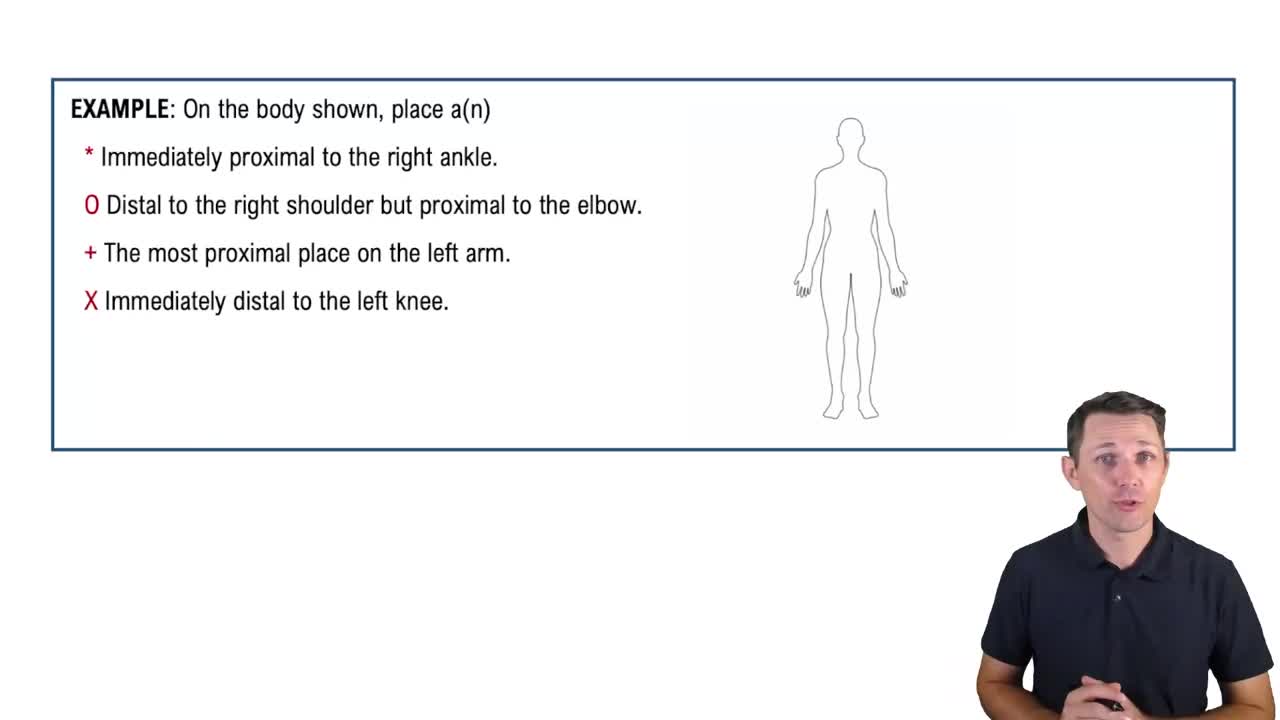
Directional Terms: Limbs Example 1
Tendon
A tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscles to bones. Tendons are designed to withstand tension and transmit the force generated by muscle contractions to the skeletal system, facilitating movement. Their structure is primarily composed of collagen fibers, which provide strength and durability, making them essential for efficient locomotion and stability.
Recommended video:
Aponeurosis
An aponeurosis is a broad, flat sheet of connective tissue that serves a similar function to a tendon but covers a larger area. It connects muscles to the parts they move, such as bones or other muscles, and provides a means for muscle force distribution over a wider surface. Aponeuroses are particularly important in areas where muscles need to exert force over a broad region, such as the abdominal wall.
Recommended video:
Organization of Muscle Tissue
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance