Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Forearm Muscles
The forearm contains several muscles that are responsible for the movement of the wrist and fingers. These muscles can be categorized into flexors and extensors, with extensors primarily located on the posterior side of the forearm. Understanding the anatomy and function of these muscles is crucial for identifying which ones act as powerful extensors and abductors of the hand.
Recommended video:
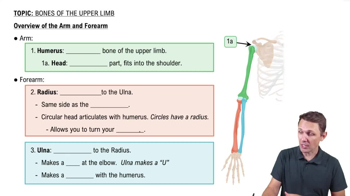
Overview of the Arm and Forearm
Extensors and Abductors
Extensors are muscles that increase the angle between body parts, such as straightening the wrist or fingers. Abductors, on the other hand, are responsible for moving a limb away from the midline of the body. In the context of the forearm, certain extensor muscles also contribute to the abduction of the hand, which is essential for various hand movements.
Recommended video:
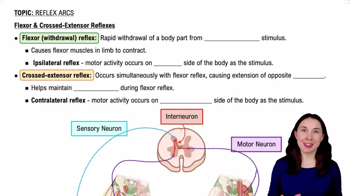
Flexor & Crossed-Extensor Reflexes
Distal Interphalangeal Joints
The distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints are the joints located between the last two phalanges of the fingers. Flexing these joints allows for gripping and fine motor tasks. The sole muscle capable of flexing the DIP joints is the flexor digitorum profundus, which plays a critical role in hand function and dexterity.
Recommended video:
Structural Joint Classifications
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance