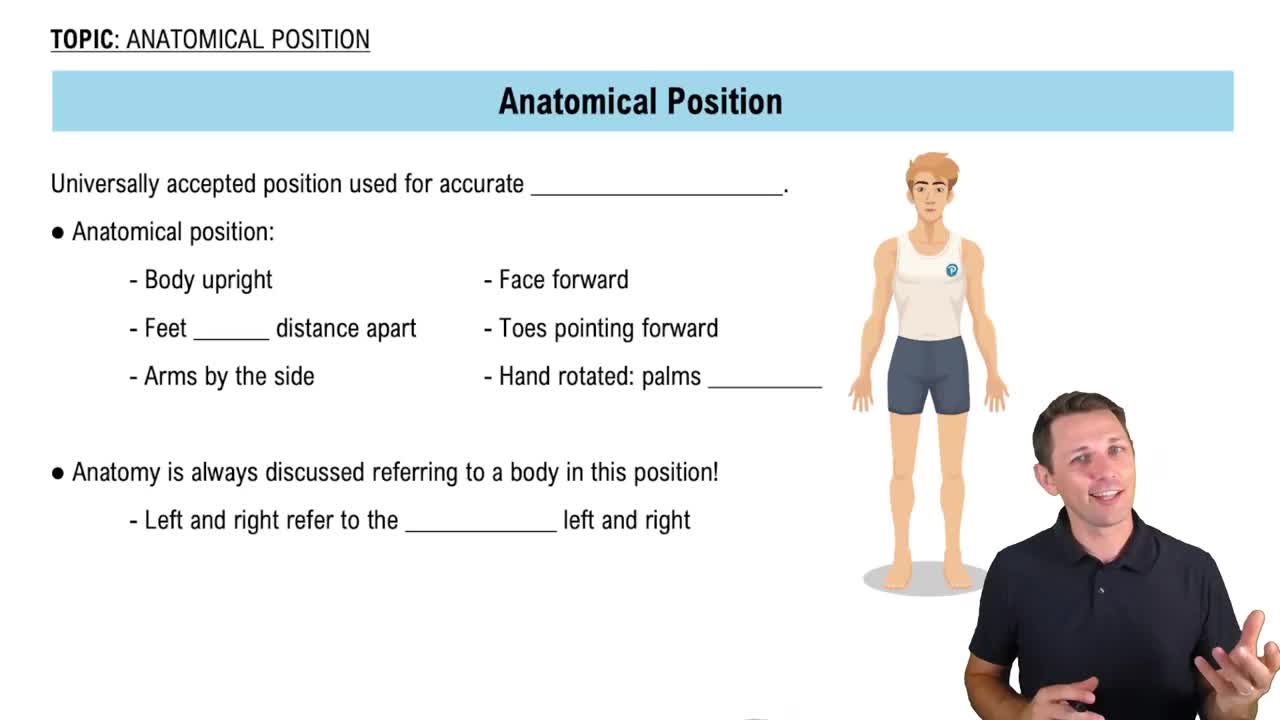
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Visceral and Parietal Membranes
Visceral and parietal membranes are two types of serous membranes that line body cavities and cover organs. The visceral membrane directly covers the organs, while the parietal membrane lines the cavity walls. Understanding the distinction between these two types is crucial for identifying anatomical relationships correctly.
Recommended video:
Peritoneum, Pericardium, and Pleura
The peritoneum, pericardium, and pleura are specific serous membranes associated with different body cavities. The peritoneum surrounds the abdominal cavity, the pericardium encloses the heart, and the pleura covers the lungs and lines the thoracic cavity. Recognizing which membrane corresponds to which organ or cavity is essential for evaluating the relationships presented in the question.
Recommended video:
Organization of the Body: Serous Membrane Locations Example 1
Anatomical Relationships
Anatomical relationships refer to the spatial and functional connections between different structures in the body. Understanding these relationships helps in identifying correct pairings, such as which membrane covers which organ. Analyzing these relationships is key to determining the accuracy of the options provided in the question.
Recommended video: