Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
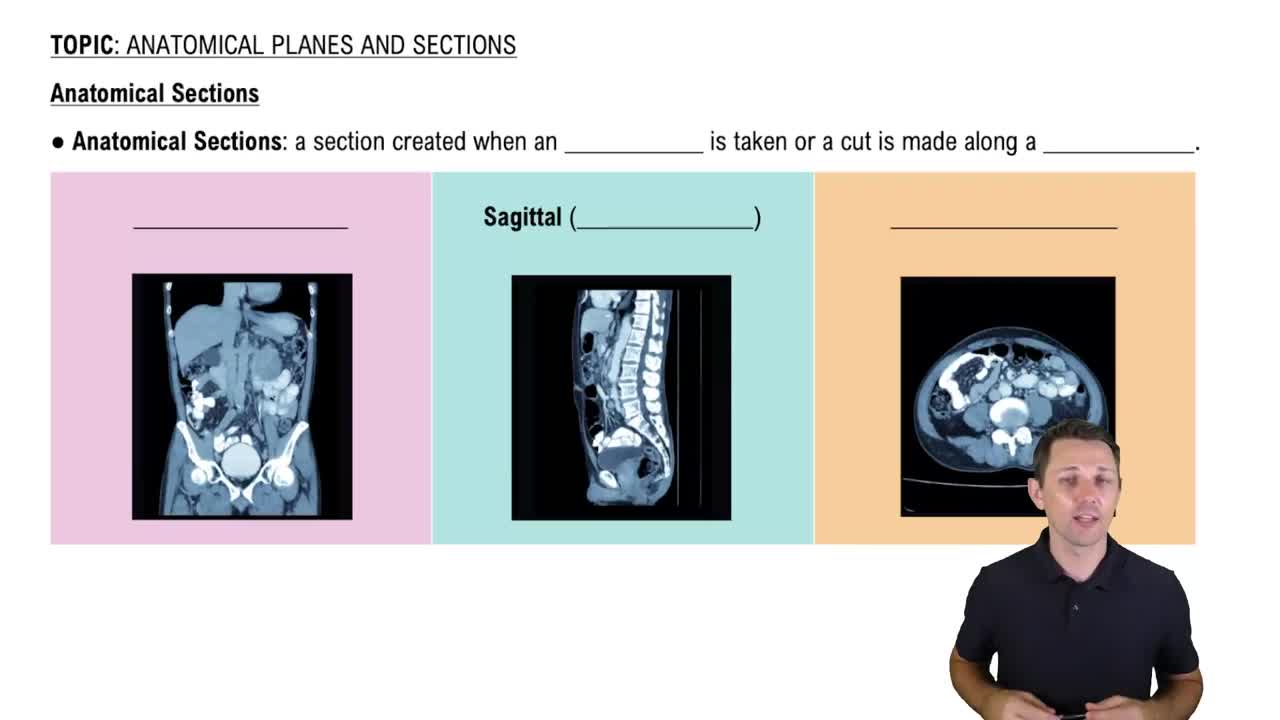
Anatomical Planes
Anatomical planes are imaginary lines that divide the body into sections, aiding in the study of anatomy. The median plane divides the body into left and right halves, the frontal plane separates the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections, and the transverse plane cuts the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts. Understanding these planes is crucial for visualizing the location of organs in relation to one another.
Recommended video:
Organ Location and Orientation
Different organs are situated in specific locations within the body, which affects their visibility when sectioned along anatomical planes. For instance, the brain is located in the cranial cavity and would be visible in the median and frontal planes, while the urinary bladder is located in the pelvic cavity and may only be visible in the transverse plane. Recognizing the orientation of each organ helps determine which planes reveal them.
Recommended video:
Organization of the Body: Serous Membrane Locations Example 1
Cross-Sectional Imaging
Cross-sectional imaging techniques, such as CT scans or MRIs, utilize the concept of anatomical planes to visualize internal structures. By slicing the body along these planes, healthcare professionals can assess the visibility of organs and identify abnormalities. This concept is essential for understanding how different imaging modalities can provide insights into organ placement and health.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance