Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis refers to the biological process through which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This involves various physiological mechanisms that regulate factors such as temperature, pH, and electrolyte balance, ensuring optimal conditions for cellular functions. Understanding homeostasis is crucial for analyzing how feedback mechanisms operate to sustain life.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Homeostasis
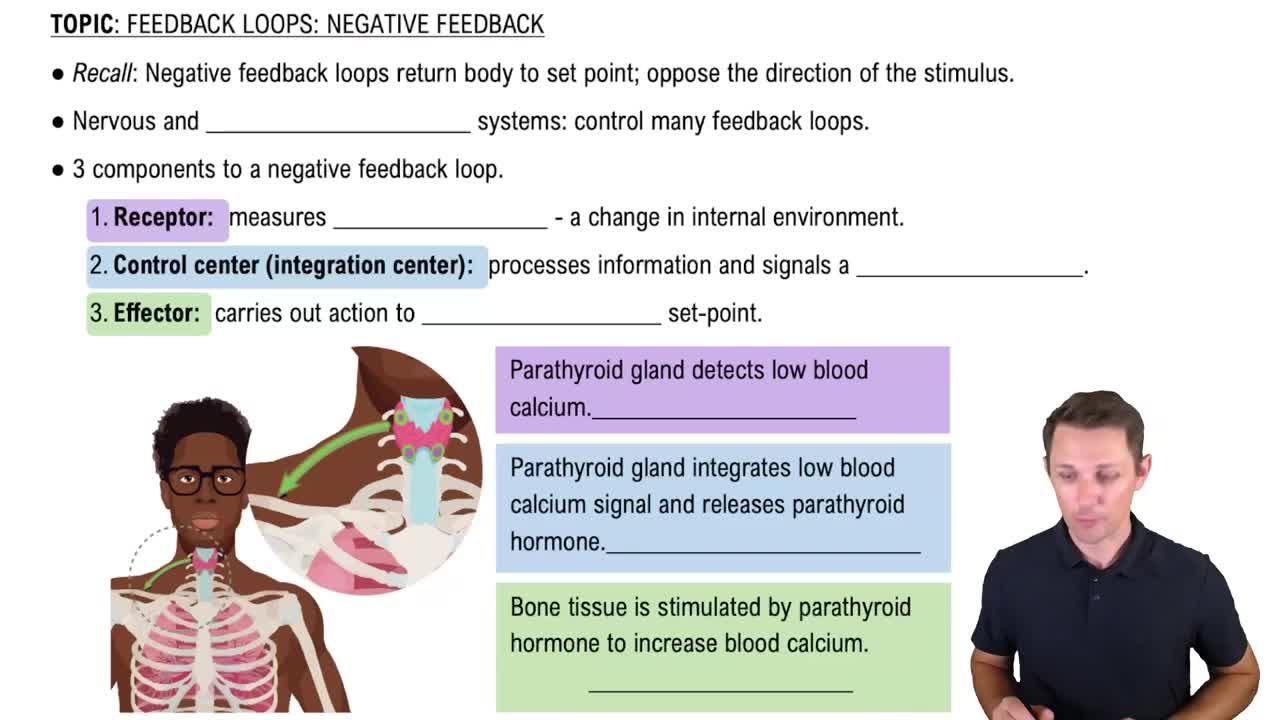
Negative Feedback Mechanism
Negative feedback mechanisms are processes that counteract changes in a system to restore equilibrium. When a variable deviates from its set point, sensors detect the change and trigger responses that reverse the direction of the deviation. For example, in temperature regulation, if body temperature rises, mechanisms such as sweating are activated to cool the body down, illustrating how negative feedback maintains homeostasis.
Recommended video:
Positive Feedback Mechanism
Positive feedback mechanisms amplify changes in a system rather than counteracting them, leading to a greater deviation from the initial state. This type of feedback is less common but plays a critical role in specific processes, such as childbirth, where the release of oxytocin increases contractions, further stimulating its own release. Understanding positive feedback is essential for recognizing how certain biological processes can escalate to achieve a specific outcome.
Recommended video:
Feedback Loops: Positive Feedback Example 1