Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
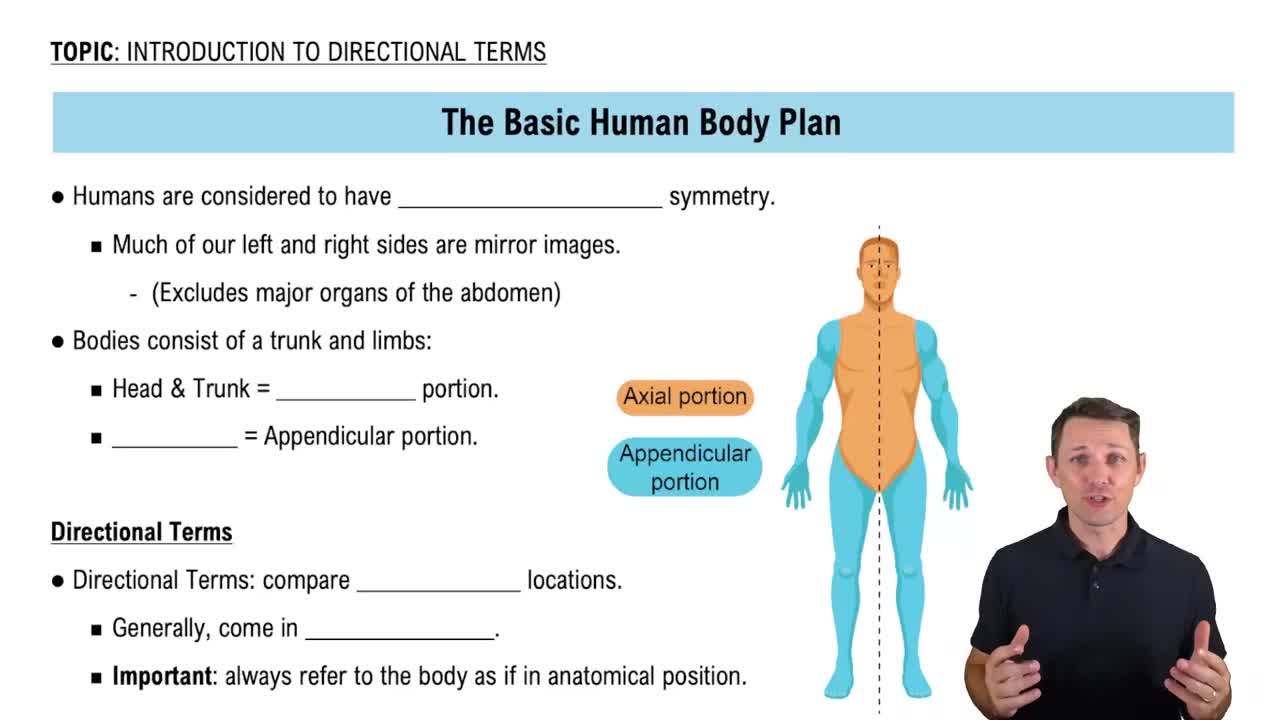
Directional Terms
Directional terms are specific words used to describe the location of one body part in relation to another. Common terms include 'superior' (above), 'inferior' (below), 'medial' (toward the midline), and 'lateral' (away from the midline). These terms provide a standardized way to communicate anatomical relationships, which is essential for clarity in fields like anatomy and medicine.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Directional Terms
Olecranal Region
The olecranal region refers to the area of the elbow, specifically the bony prominence known as the olecranon. This region is located posteriorly to the forearm and is crucial for understanding the arm's structure and movement. Recognizing its position helps in describing how it relates to other parts of the arm, such as the palm.
Recommended video:
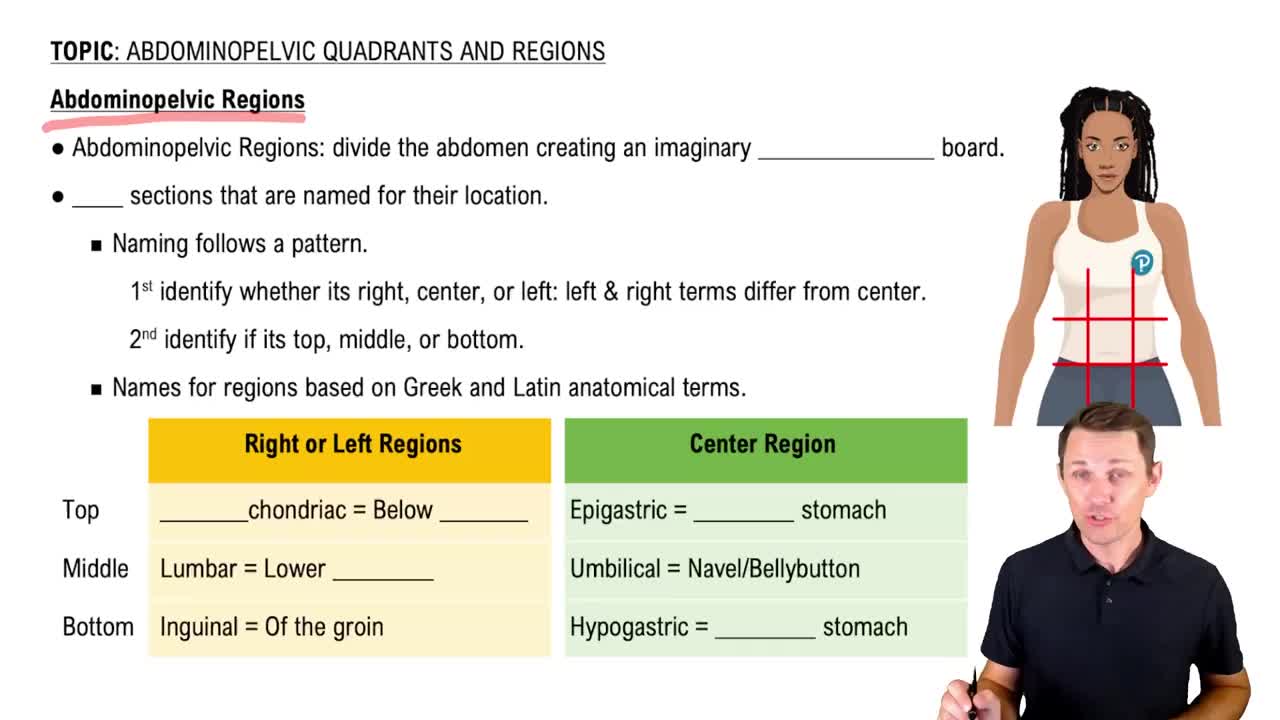
The 9 Abdominopelvic Regions
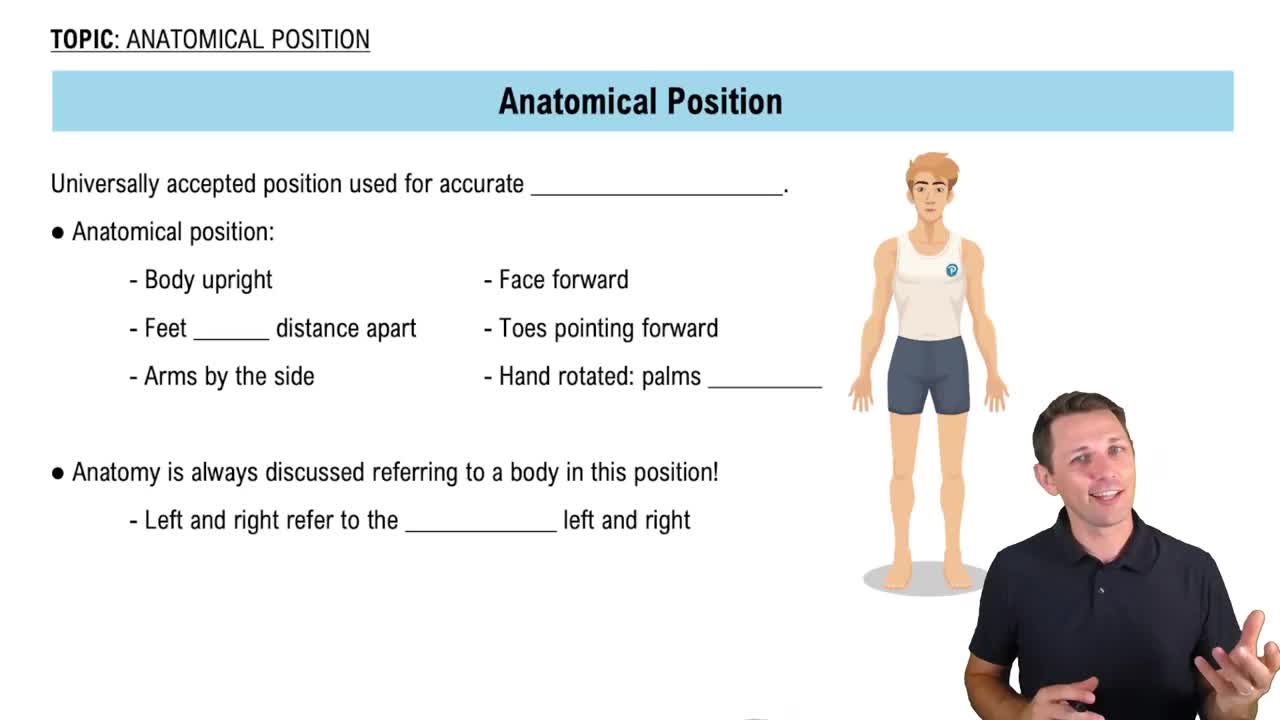
Anatomical Position
The anatomical position is a standard reference point in anatomy where the body is standing upright, facing forward, with arms at the sides and palms facing forward. This position serves as a baseline for using directional terms, allowing for consistent descriptions of the relationships between body parts, such as the olecranal region and the palm.
Recommended video:
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
Ch. 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Problem 20
Problem 20 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance