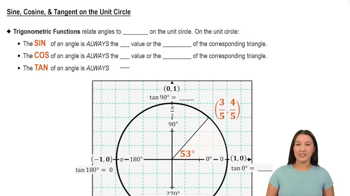
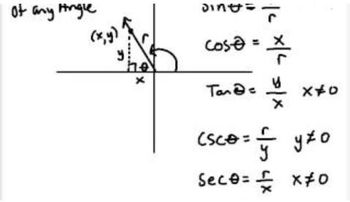
3. Unit Circle
Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
3. Unit Circle
Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Find the sine, cosine, and tangent of each angle using the unit circle.
rad,
719views4rank - Multiple Choice
Find the sine, cosine, and tangent of each angle using the unit circle.
767views2rank - Textbook QuestionFind exact values of the six trigonometric functions for each angle A.648views
- Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Match each trigonometric function in Column I with its value in Column II. Choices may be used once, more than once, or not at all. I II1. A. √32. B. 13. tan 45° C. ½4. D. √35. 26. E. 2√3 3 F. √3 3 G. 2 H. √2 2 I. √2588views
- Textbook Question
Find each exact function value. See Example 2. sin 7π/6
843views - Textbook Question
Graph each function over a one-period interval.
y = - (1/2) csc (x + π/2)
758views - Multiple Choice
On the unit circle, which trigonometric functions are undefined when ?
29views - Multiple Choice
On the unit circle, which of the following points would map onto itself after a reflection across the line ?
50views