Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Focal Length
Focal length is the distance from the lens to the point where parallel rays of light converge or appear to diverge. It is a critical parameter in optics that determines how strongly a lens converges or diverges light. For corrective lenses, the focal length is essential for ensuring that light focuses correctly on the retina, allowing for clear vision.
Recommended video:
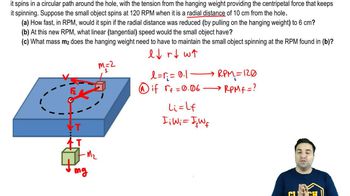
Spinning on a string of variable length
Lens Power
Lens power, measured in diopters (D), is the reciprocal of the focal length in meters. It indicates the degree of convergence or divergence of light by the lens. A positive power indicates a converging lens (convex), while a negative power indicates a diverging lens (concave). The power is crucial for determining the appropriate lens needed to correct vision.
Recommended video:
Optical Correction
Optical correction involves using lenses to adjust the focal point of light entering the eye, compensating for refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness). The goal is to ensure that light focuses directly on the retina, improving visual clarity. Understanding the relationship between the distance of the lens from the eye and the required focal length is vital for effective correction.
Recommended video: