Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Focal Length
The focal length of a lens is the distance from the lens to the point where parallel rays of light converge or appear to diverge. For a thin lens, this distance is crucial in determining how the lens will magnify an object. In this case, a focal length of 6.00 cm indicates that the lens can focus light at this distance, which is essential for calculating magnification.
Recommended video:
Spinning on a string of variable length
Angular Magnification
Angular magnification is a measure of how much larger an object appears when viewed through a lens compared to the naked eye. It is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the image at the eye to the angle subtended by the object at the same eye without the lens. For a simple magnifier, this is particularly relevant when the object is placed at the focal point, maximizing the apparent size of the image.
Recommended video:
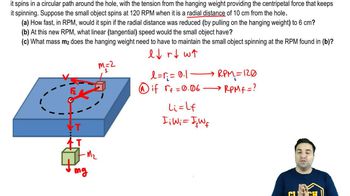
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Simple Magnifier
A simple magnifier is a type of optical device, typically a convex lens, used to enlarge the appearance of an object. When an object is placed at or near the focal point of the lens, the lens produces a virtual image that appears larger than the object itself. Understanding how a simple magnifier works is essential for calculating the angular magnification in this scenario.
Recommended video:
Simple Harmonic Motion of Pendulums