Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. This relationship is expressed mathematically as I = V/R. Understanding this law is crucial for analyzing electrical circuits, as it allows us to calculate the current based on the applied voltage and the total resistance in the circuit.
Recommended video:
Series and Parallel Resistor Configurations
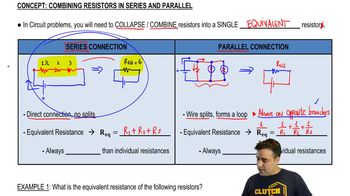
Resistors can be arranged in series or parallel configurations, affecting the total resistance in the circuit. In a series configuration, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances (R_total = R1 + R2 + ...). In a parallel configuration, the total resistance can be calculated using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... This distinction is essential for determining how the resistors in the given circuit will influence the overall current drawn from the battery.
Recommended video:
Combining Resistors in Series & Parallel
Equivalent Resistance
Equivalent resistance is the total resistance that a circuit presents to the battery or power source. It simplifies complex resistor networks into a single resistance value, making it easier to analyze the circuit. For the triangular array of resistors shown, calculating the equivalent resistance is necessary to determine how much current will flow from the 35.0-V battery when connected across points a and b.
Recommended video:
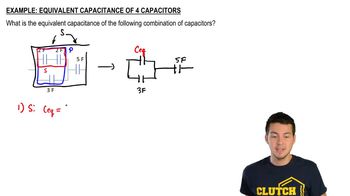
Find Equivalent Capacitance #1

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance