Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
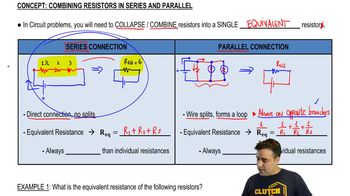
Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits
In electrical circuits, resistors can be arranged in series or parallel configurations. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance can be calculated using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... + 1/Rn. Understanding these configurations is crucial for analyzing the overall resistance in complex circuits.
Recommended video:
Combining Resistors in Series & Parallel
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. This relationship is expressed as V = IR. It is fundamental in circuit analysis, allowing us to relate voltage, current, and resistance.
Recommended video:
Equivalent Resistance
Equivalent resistance is the total resistance of a circuit when multiple resistors are combined. For resistors in series, the equivalent resistance is simply the sum of the individual resistances. For resistors in parallel, the equivalent resistance is found using the reciprocal formula. This concept is essential for simplifying complex circuits to determine the overall resistance between two points.
Recommended video:
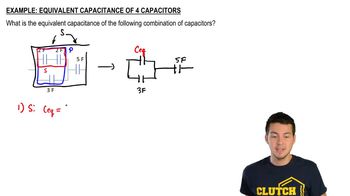
Find Equivalent Capacitance #1

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance