Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. This relationship is expressed mathematically as I = V/R. Understanding this law is crucial for calculating the current in the resistor network when a voltage is applied.
Recommended video:
Series and Parallel Resistor Combinations
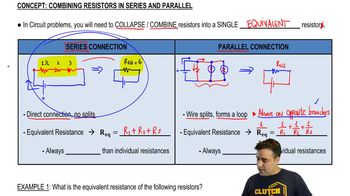
Resistors can be combined in series or parallel configurations, affecting the total resistance in a circuit. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance can be found using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... + 1/Rn. Recognizing how the resistors in the triangular array are arranged is essential for determining the equivalent resistance and, subsequently, the current drawn from the battery.
Recommended video:
Combining Resistors in Series & Parallel
AC vs. DC Circuits
Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) circuits behave differently due to the nature of the current flow. In AC circuits, the current changes direction periodically, while in DC circuits, the current flows in one direction. The question specifies connecting the resistor array to an AC source, which may involve additional considerations such as impedance and phase differences, impacting the overall current calculation.
Recommended video: