Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acceleration
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity over time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. In this context, it can be calculated using the formula a = (v_f - v_i) / t, where v_f is the final velocity, v_i is the initial velocity, and t is the time taken for that change. Understanding acceleration is crucial for analyzing the rocket's motion during its launch.
Recommended video:
Units of Measurement
In physics, it is essential to use consistent units when performing calculations. The problem involves weights in pounds and speeds in kilometers per hour, which need to be converted to standard SI units (meters, kilograms, seconds) for accurate calculations. For instance, 1 pound is approximately 0.453592 kilograms, and 1 kilometer per hour is approximately 0.277778 meters per second. Proper unit conversion ensures that the results are meaningful and comparable.
Recommended video:
Average vs. Instantaneous Values
Average values represent the total change over a period divided by the time taken, while instantaneous values refer to the measurement at a specific moment. In this question, average acceleration is calculated for two distinct time intervals: the first 8 seconds and from 8 seconds to 1 minute. Recognizing the difference between these two types of measurements is vital for accurately interpreting the rocket's performance during its launch phases.
Recommended video:
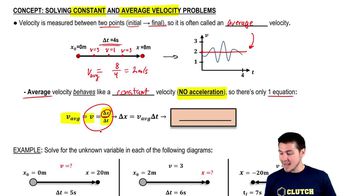
Solving Constant and Average Velocity Problems
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance