Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acceleration
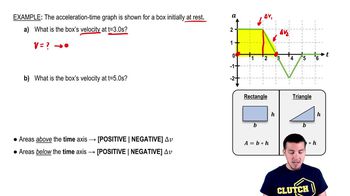
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. In the context of the provided graph, the acceleration values indicate how quickly the particle's velocity is changing over time, which is crucial for determining the particle's velocity at any given moment.
Recommended video:
Velocity from Acceleration
To find the velocity of a particle from its acceleration, one must integrate the acceleration function over time. Since the particle starts from rest, the initial velocity is zero. The area under the acceleration-time graph represents the change in velocity, allowing us to calculate the particle's velocity at specific time intervals by summing the areas under the curve.
Recommended video:
Calculating Change in Velocity from Acceleration-Time Graphs
Graph Interpretation
Interpreting graphs is essential in physics for understanding the relationships between different physical quantities. In this case, the acceleration graph provides insights into how the particle's acceleration varies over time. By analyzing the shape and area of the graph, one can derive important information about the particle's motion, including its velocity at specific times.
Recommended video:
Graphing Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Graphs