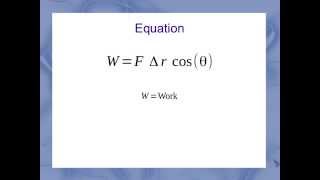9. Work & Energy
Intro to Calculating Work
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
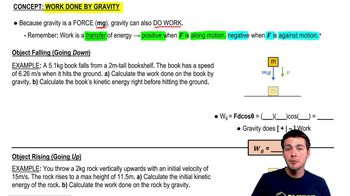
You pull a 5kg box vertically up with a constant 100N force for 2m. How much work do you do?
3073views59rank4comments - Multiple Choice
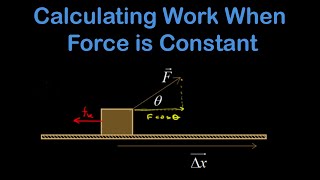
You push a 3kg box against a wall for a distance of 2m with a force of 40N that makes a 53° angle with the horizontal, as shown. Calculate the work done by gravity.
2622views54rank9comments - Multiple ChoiceA pallet of bricks is being lowered to the ground by a crane. If the bricks are moving at a constant speed, how much work is done by the cable on the bricks as they descend ?782views
- Multiple ChoiceA particle of mass moving along the x axis has velocity with x measured in m. How much work is done on the particle as it moves from to ?962views
- Textbook Question
A factory worker pushes a -kg crate a distance of m along a level floor at constant velocity by pushing horizontally on it. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is . What is the total work done on the crate?
1501views - Textbook Question
Two tugboats pull a disabled supertanker. Each tug exerts a constant force of N, one west of north and the other east of north, as they pull the tanker km toward the north. What is the total work they do on the supertanker?
2169views - Textbook Question
A factory worker pushes a -kg crate a distance of m along a level floor at constant velocity by pushing horizontally on it. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is . How much work is done on the crate by the normal force? By gravity?
2798views1rank - Textbook Question
A factory worker pushes a -kg crate a distance of m along a level floor at constant velocity by pushing horizontally on it. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is . How much work is done on the crate by this force?
2466views1rank