14. Torque & Rotational Dynamics
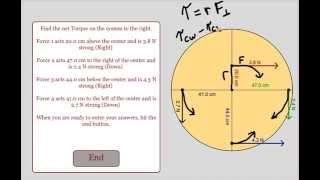
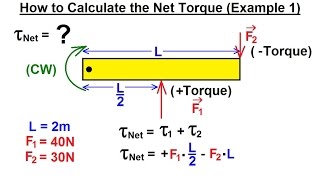
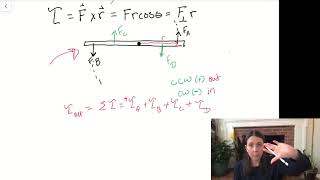
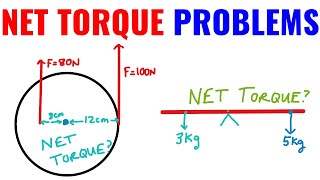
Net Torque & Sign of Torque
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A 2-m long bar is free to rotate about an axis located 0.7 m from one of its ends. Two forces act on the bar, F1 = 100 N and F2 = 200 N, and both make 30° with the bar. Find the Net Torque on the bar. Use +/− to indicate direction.
1537views33rank7comments - Textbook Question
Three forces are applied to a wheel of radius 0.350 m, as shown in Fig. E10.4. One force is perpendicular to the rim, one is tangent to it, and the other one makes a 40.0° angle with the radius. What is the net torque on the wheel due to these three forces for an axis perpendicular to the wheel and passing through its center?
2665views1rank1comments - Textbook Question
A 1.0 kg ball and a 2.0 kg ball are connected by a 1.0-m-long rigid, massless rod. The rod is rotating cw about its center of mass at 20 rpm. What net torque will bring the balls to a halt in 5.0 s?
3664views - Textbook Question
An object's moment of inertia is 2.0 kg m2. Its angular velocity is increasing at the rate of 4.0 rad/s per second. What is the net torque on the object?
1515views - Textbook Question
A satellite follows the elliptical orbit shown in FIGURE P12.77. The only force on the satellite is the gravitational attraction of the planet. The satellite's speed at point 1 is 8000 m/s. Does the satellite experience any torque about the center of the planet? Explain.
1231views