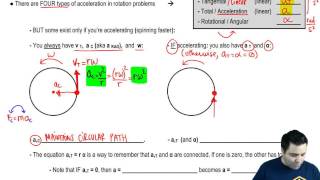
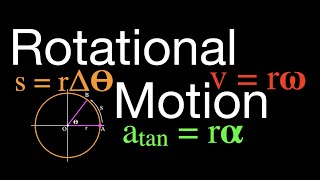
12. Rotational Kinematics
Types of Acceleration in Rotation
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A large disc of radius 10 m initially at rest takes 200 full revolutions to reach 30 RPM. Calculate the total linear acceleration of a point at half way between the disc's center and its edge, once the disc reaches 30 RPM. (You may assume it continues accelerating past that point)
1518views22rank2comments - Multiple Choice
An object of negligible size moves in a circular path of radius 20 m with 90 RPM. Find its radial acceleration.
1494views26rank3comments - Multiple ChoiceA person is spinning a baton in their hand. The baton goes from rest to rotating at 2.7 rotations per second in 2.0 seconds. What is the angular acceleration of the baton?1064views
- Multiple ChoiceA certain carnival ride is spinning, and smoothly changes its motion from clockwise to counterclockwise, stopping only for an instant in the middle. In this instant, which of the following is correct?1201views
- Textbook Question
An object of mass m is constrained to move in a circle of radius r. Its tangential acceleration as a function of time is given by atan = b + ct2, where b and c are constants. If v = v0 at t = 0, determine the tangential and radial components of the force, Ftan and FR, acting on the object at any time t > 0.
1044views - Textbook Question
You are driving your 1800 kg car at 25 m/s over a circular hill that has a radius of 150 m. A deer running across the road causes you to hit the brakes hard while right at the summit of the hill, and you start to skid. The coefficient of kinetic friction between your tires and the road is 0.75. What is the magnitude of your acceleration as you begin to slow?
2611views - Textbook Question
A toy train rolls around a horizontal 1.0-m-diameter track. The coefficient of rolling friction is 0.10. How long does it take the train to stop if it's released with an angular speed of 30 rpm?
1776views - Textbook Question
A new car is tested on a 200-m-diameter track. If the car speeds up at a steady 1.5 m/s2, how long after starting is the magnitude of its centripetal acceleration equal to the tangential acceleration?
1892views